By DR KOH SOO LING
Information transfer from graphic representation to text
Common problems related to describing and interpreting graphic representations are:
• Not Understanding the Data (I) — Not Reading the Labels: Students do not correctly understand the data in the charts: often they do not read the labels carefully (e.g. student writes “12 people were injured in the recent tsunami”, when they should write “120 people were injured in the recent tsunami”).
• Not Understanding the Data (II) — Not Applying Common Sense to Your Interpretations: Students do not apply common sense to the interpretation of data in the charts (e.g. in the example above, it is unlikely that only 12 people were injured in the recent tsunami; we should then analyse the chart carefully to find a more satisfactory interpretation).
• Just “Listing” the Data: Students simply “list” data from charts or graphs without trying to indicate what is more or less important. You should take note of large differences or changes and present them first.
• Not “Translating” Note Form to Grammatical English: Labels or titles are usually in note form, so you need to change them into grammatically correct English in your writing. For example, in a chart entitled the danger of obesity in Malaysia, one label may be the number of people affected by the disease. It would therefore be ungrammatical to say “the number of obesity people”; we need to change that to the number of obese people instead.
Practice A
Choose the best option to make the sentences grammatically correct:
1. The main reason that young people (shoplift/shoplifts) is because they want to prove that they can get away with a crime.
2. Shoplifting is a crime that is present in (any/some) country.
3. Retailers (report/reports) that 0.6 per cent of all missing inventory are due to shoplifters.
4. In 2001, shoplifting (cost/ costs) US retailers US$25 million (RM75 million) a day.
5. Retailers focusing on loss (preventing/prevention) often devote most of their resources to closed-circuit television.
6. It is one of the most common property crimes (dealt/deal) with by police and courts.
7. Most shoplifters are amateurs; however, there are people and groups who make their (lives/living) from shoplifting,
8. Many big retail or grocery stores have a loss (prevent/prevention) officer to keep an eye out for shoplifters.
9. Trained staff know the basics, observe the person, observe the item, note the concealment and wait until the shoplifter (leave/ leaves) the store to make the arrest.
10. If apprehended during the shoplifting, the merchandise is generally (recover/recovered) by the retailers.
Next week: Speaking strategies I
ANSWERS:
1. shoplifts
2. any
3. report
4. cost
5. prevention
6. dealt
7. living
8. prevention
9. leaves
10. recovered
Source: Learning Curve - New Straits Times
Click here to enter your email for more SPM 2019 tips and sample essays! Free essay writing guide on how to write an essay in five simple steps. Good essays, essay writing, essay examples, essay topics & essay guide. Improve your writing skill and become an effective writer. Model essays for GCE O Level, A Level, SPM English 1119, SPM EST, STPM MUET, IELTS Writing & TOEFL
Monday, May 28, 2012
Monday, May 21, 2012
MUET MOMENTS: Lesson 9: Information transfer from graphic representation to text
By DR KOH SOO LING
Information transfer from graphic representation to text


Study and understand the graphic representation to know the general idea. You can ask questions like, "What is the main subject? " "What is documented along the X/Y axis?" You can also look for extreme points of data, for example, the highest, the lowest, the greatest or the smallest.
Remember to look for details along the vertical axis or the horizontal axis. You can also obtain information from the title, source, legend and scale.
Vocabulary for Describing Trends
1. Downward movement
decline, crash, decrease, collapse, drop, plummet, fall, plunge, slide, fall, plunge, slide, take a fall, lose ground, weaken
2. Upward movement
climb, soar, rise, gain, increase, go though the roof, surge, jump, rocket, rally, strengthen, high
3. Stability
flatten out, bounce back, hold steady, rally, level off, recover, stabilise, stable
4. To specify the degree of change
slow, disastrous, steady, massive, slight, perilous, sharp, rapid, gradual, heavy, low
Population of Country X from 2003 to 2007
The table shows the population of Country X from 2003 to 2007. You can see that in 2003 the population was 5.25 million and that by the year 2007 it had grown to 5.45 million. There was an increase of 0.2 million or 200,000 people. We can see that the population of Country X increased gradually from 2003 to 2007.
Example 2
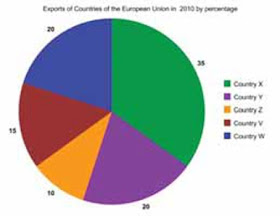
These two charts show the relative size of exports by percentage of countries of the European Union in 2009 and 2010.
The first thing to notice is that there is very little change: the minimum change is 2% and the maximum change is 4%. The second change to notice is which countries' exports grew (as a proportion of the whole) and which countries' exports shrank.
You can see that the exports of Countries X, Y and Z fell from 2009 to 2010 (from 37% to 35%, from 22% to 30% and from 12% to 10% respectively).
The largest growth in export share was that of Country V which increased its share from 11% to 15%. Country W's share of the EU export percentage grew by 2%.
In spite of the change in Country X's export percentage, it remained the largest export percentage share of the European Union.
Next Week: Information Transfer II
Source: Learning Curve - New Straits Times
Information transfer from graphic representation to text



Study and understand the graphic representation to know the general idea. You can ask questions like, "What is the main subject? " "What is documented along the X/Y axis?" You can also look for extreme points of data, for example, the highest, the lowest, the greatest or the smallest.
Remember to look for details along the vertical axis or the horizontal axis. You can also obtain information from the title, source, legend and scale.
Vocabulary for Describing Trends
1. Downward movement
decline, crash, decrease, collapse, drop, plummet, fall, plunge, slide, fall, plunge, slide, take a fall, lose ground, weaken
2. Upward movement
climb, soar, rise, gain, increase, go though the roof, surge, jump, rocket, rally, strengthen, high
3. Stability
flatten out, bounce back, hold steady, rally, level off, recover, stabilise, stable
4. To specify the degree of change
slow, disastrous, steady, massive, slight, perilous, sharp, rapid, gradual, heavy, low
Population of Country X from 2003 to 2007
The table shows the population of Country X from 2003 to 2007. You can see that in 2003 the population was 5.25 million and that by the year 2007 it had grown to 5.45 million. There was an increase of 0.2 million or 200,000 people. We can see that the population of Country X increased gradually from 2003 to 2007.
Example 2
These two charts show the relative size of exports by percentage of countries of the European Union in 2009 and 2010.
The first thing to notice is that there is very little change: the minimum change is 2% and the maximum change is 4%. The second change to notice is which countries' exports grew (as a proportion of the whole) and which countries' exports shrank.
You can see that the exports of Countries X, Y and Z fell from 2009 to 2010 (from 37% to 35%, from 22% to 30% and from 12% to 10% respectively).
The largest growth in export share was that of Country V which increased its share from 11% to 15%. Country W's share of the EU export percentage grew by 2%.
In spite of the change in Country X's export percentage, it remained the largest export percentage share of the European Union.
Next Week: Information Transfer II
Source: Learning Curve - New Straits Times
Monday, May 14, 2012
MUET MOMENTS: Lesson 8: Understanding sense relationships — Text cohesion
By DR KOH SOO LING
Understanding sense relationships — Text cohesion
It is important for a writer to make sure that the text that he writes makes sense to the reader. This means that he should ensure that the sentences he writes are well connected and related to the main topic that he has in mind.
Linking words or discourse markers are cohesive devices. With the use of linking words, sentences can be put together for easy comprehension. See the table below:
Practice
Fill in each of the blanks with an appropriate discourse marker.
Media studies is an academic discipline and field of study that deal with the content, history (1)________________ effects of various media; in particular, the “mass media”. Researchers may develop and employ theories and methods from disciplines (2)_______________ cultural studies, rhetoric, philosophy, literary theory, psychology and political science.
Separate strands exist within media studies, (3)____________ television studies. Contemporary media studies includes the analysis of new media with emphasis on the Internet, video games, mobile devices, interactive television and other forms of mass media which developed from the 1990s. (4)_______________ these new technologies allow instant communication across the world (chat rooms and instant messaging, online video games, video conferencing), interpersonal communication is an important element in new media studies.
In secondary schools, an early “film studies” course was (5)____________ taught as part of the Victorian junior secondary curriculum during the mid 1960s.
By the early 1970s, an expanded “media studies” course was being taught. Due to its success, the course (6)_______________ became part of the senior secondary curriculum.
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Media_studies
Next week: Information Transfer from graphic Representation to text
ANSWERS:
1. and
2. such as
3. for example
4. because
5. first
6. subsequently
Source: Learning Curve - New Straits Times
Understanding sense relationships — Text cohesion
It is important for a writer to make sure that the text that he writes makes sense to the reader. This means that he should ensure that the sentences he writes are well connected and related to the main topic that he has in mind.
Linking words or discourse markers are cohesive devices. With the use of linking words, sentences can be put together for easy comprehension. See the table below:
Practice
Fill in each of the blanks with an appropriate discourse marker.
Media studies is an academic discipline and field of study that deal with the content, history (1)________________ effects of various media; in particular, the “mass media”. Researchers may develop and employ theories and methods from disciplines (2)_______________ cultural studies, rhetoric, philosophy, literary theory, psychology and political science.
Separate strands exist within media studies, (3)____________ television studies. Contemporary media studies includes the analysis of new media with emphasis on the Internet, video games, mobile devices, interactive television and other forms of mass media which developed from the 1990s. (4)_______________ these new technologies allow instant communication across the world (chat rooms and instant messaging, online video games, video conferencing), interpersonal communication is an important element in new media studies.
In secondary schools, an early “film studies” course was (5)____________ taught as part of the Victorian junior secondary curriculum during the mid 1960s.
By the early 1970s, an expanded “media studies” course was being taught. Due to its success, the course (6)_______________ became part of the senior secondary curriculum.
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Media_studies
Next week: Information Transfer from graphic Representation to text
ANSWERS:
1. and
2. such as
3. for example
4. because
5. first
6. subsequently
Source: Learning Curve - New Straits Times
Monday, May 07, 2012
MUET MOMENTS: Lesson 7: Understanding Sense Relationships - Reference Words
By DR KOH SOO LING
Understanding Sense Relationships -- Reference Words
WRITERS create cohesion throughout a text by using reference words. Reference words reintroduce, manipulate or anticipate information continually and in interesting ways. They consist mainly of pronouns and noun phrases which represent other elements in a text.
Reference words cannot stand alone; rather, they need to connect with other words to complete their meanings.
They are used when new information is added about the things that they refer to, therefore, the term "reference words".
Practice
Read the passage below. What do the words in bold refer to?
Food safety is a scientific discipline describing the process of handling, preparation, and storage of food to prevent food borne illness. This includes a number of routines that should be followed to avoid potentially severe health hazards. Food can transmit disease from person to person as well as serve as a growth medium for bacteria that can cause food poisoning. Genetic pollution of environment, which can destroy natural biological diversity, is of great significance. In developed countries, there are intricate standards for food preparation, whereas in lesser developed countries, the main issue is simply the availability of adequate safe water.
One of the simplest measures that a person can take to prevent the spread of food borne illness is to properly wash his hands before preparing or eating any meal. Many people who believe they are adequately washing their hands are sorely mistaken. According to a study conducted by the American Society of Microbiology, 97 per cent of females said they washed their hands, but those numbers turned out to be 75 per cent of females upon observation. Some foods should simply never be ingested in the first place because these have such a high risk of containing harmful bacteria that can make people ill. Cross contamination occurs when a person handling raw meats, eggs, fish or other foods containing harmful pathogens touches cooking utensils, cutting boards or cooking surfaces and spreads the pathogens to ready-to-eat foods in the process. This mode of transmission can be interrupted by washing hands after handling raw foods, washing utensils and cutting boards that have come in contact with raw foods, and disinfecting counter surfaces frequently.
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_safety
1. this
2. which
3. the main issue
4. his
5. they
6. their
7. these
8. this mode of transmission
NEXT WEEK: Understanding Sense Relationships -- Text Cohesion
Source: Learning Curve - New Straits Times
Understanding Sense Relationships -- Reference Words
WRITERS create cohesion throughout a text by using reference words. Reference words reintroduce, manipulate or anticipate information continually and in interesting ways. They consist mainly of pronouns and noun phrases which represent other elements in a text.
Reference words cannot stand alone; rather, they need to connect with other words to complete their meanings.
They are used when new information is added about the things that they refer to, therefore, the term "reference words".
Practice
Read the passage below. What do the words in bold refer to?
Food safety is a scientific discipline describing the process of handling, preparation, and storage of food to prevent food borne illness. This includes a number of routines that should be followed to avoid potentially severe health hazards. Food can transmit disease from person to person as well as serve as a growth medium for bacteria that can cause food poisoning. Genetic pollution of environment, which can destroy natural biological diversity, is of great significance. In developed countries, there are intricate standards for food preparation, whereas in lesser developed countries, the main issue is simply the availability of adequate safe water.
One of the simplest measures that a person can take to prevent the spread of food borne illness is to properly wash his hands before preparing or eating any meal. Many people who believe they are adequately washing their hands are sorely mistaken. According to a study conducted by the American Society of Microbiology, 97 per cent of females said they washed their hands, but those numbers turned out to be 75 per cent of females upon observation. Some foods should simply never be ingested in the first place because these have such a high risk of containing harmful bacteria that can make people ill. Cross contamination occurs when a person handling raw meats, eggs, fish or other foods containing harmful pathogens touches cooking utensils, cutting boards or cooking surfaces and spreads the pathogens to ready-to-eat foods in the process. This mode of transmission can be interrupted by washing hands after handling raw foods, washing utensils and cutting boards that have come in contact with raw foods, and disinfecting counter surfaces frequently.
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_safety
1. this
2. which
3. the main issue
4. his
5. they
6. their
7. these
8. this mode of transmission
NEXT WEEK: Understanding Sense Relationships -- Text Cohesion
Source: Learning Curve - New Straits Times